|
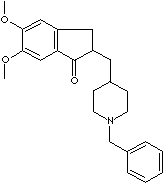
DONEPEZIL HYDROCHLORIDE |
| 1-Benzyl-4-((5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanon)-2-yl)methylpiperidine hydrochloride; 2,3-Dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-((1- (phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl) methyl)-1H-inden-1-one; Aricept; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
120014-06-4 (parent); 120011-70-3; 142057-77-0 (HCl) |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C24H29NO3· HCl |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
415.95 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
Piperidine derivative |
| CATEGORIES |
Alzheimer's disease treatment |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
yellow crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
211 - 212 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble (Soluble in chloroform, acetic acid; sparingly soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in ethanol and in acetonitrile; practically insoluble in ethyl acetate and in n-hexane) |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBILITIES |
Strong bases |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides, Nitrogen oxides, Chloride gas |
| POLYMERIZATION | Will not occur |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL |
Oral Rat LD50: 32.6 mg/kg |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Poison |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May cause irritation. This material is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. |
|
INHALATION |
May cause irritation. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
TARGET ORGANS |
|
|
CHRONIC |
Hypersensitization |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
2811 |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1 |
| PACKING GROUP |
II |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
T |
|
RISK PHRASES |
25 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
45 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Donepezil People who have depression along with mild cognitive impairment and take the popular Alzheimer’s drug donepezil may help delay the progression to full-blown Alzheimer’s disease, according to new research. The research also found that people who are depressed with existing mild memory problems or mild cognitive impairment are more likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than those without depression. (http://psychcentral.com/) Donepezil is an oral medication used to treat Alzheimer's disease. It belongs to a class of drugs called cholinesterase inhibitors that also includes tacrine (Cognex). Scientists believe that Alzheimer's disease may result from a deficiency in chemicals (neurotransmitters) used by nerves in the brain to communicate with one another. Donepezil inhibits acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme responsible for the destruction of one neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. This leads to increased concentrations of acetylcholine in the brain, and the increased concentrations are believed to be responsible for the improvement seen during treatment with donepezil. Donepezil improves the symptoms but does not slow down the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Donepezil was approved by the FDA in 1996. (http://www.medicinenet.com/)The Food and Drug Administration has approved donepezil for treatment of the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. In Alzheimer's disease, some cells in specific regions of the brain die. Because of this cell death, these brain cells lose their ability to transmit nerve impulses. Brain cells normally transmit nerve impulses by secreting various chemicals known as neurotransmitters. Brain cells that make and secrete a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine are affected early in the course of Alzheimer's disease. Donepezil helps prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine in the brain, thus temporarily increasing its concentration. In doing so, donepezil may improve the thinking process by facilitating nerve impulse transmission within the brain. (http://www.minddisorders.com/) Alzheimer's disease is a progressive degenerative disease of the brain and is a form of dementia. Characterized by a slow, progressive decline in mental and social function, Alzheimer's disease impairs memory, thinking, judgment, and the ability to learn. Alzheimer's disease can also affect personality and the ability to make decisions. The risk of developing Alzheimer's disease increases with age and is greater for women than for men. (http://www.mercksource.com/) Pharmacological Actions:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow crystalline powder |
| ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
2.0% min |
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
| ARSENIC |
1ppm max |
|
SULFATED ASH |
1.0% max |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE |
|
|